02/05/2023
Dialysis: a key and underestimated factor for the synthesis of lipid nanoparticle by microfluidics

This research summary aims at describing the influence of the critical process parameters on the main characteristics of lipid nanoparticles when synthesized by microfluidics, with a specific focus on the influence of dialysis.
The peer reviewed article “Dialysis is a key factor modulating interactions between critical process parameters during the microfluidic preparation of lipid nanoparticles” was originally published in Colloid and Interface Science Communications in April 2023 by Ronny Vargas et al.
Abstract
Synthesis of lipid nanoparticles using microfluidics is dependent on multiple process parameters, which greatly impacts the final nanoparticle physicochemical characteristics such as size, polydispersity index and zeta potential. This study uses a Design of Experiment approach to determine the influence of the total flow rate (TFR), flow rate ratio (FRR) and dialysis on the final nanoparticle parameters produced in a microfluidic herringbone mixer. The work shows that dialysis has a major impact on most nanoparticle characteristics and should be considered as early as possible in the drug discovery process.
Introduction | Impact of synthesis parameters and dialysis on nanoparticles characteristics
Microfluidics has recently been widely used for the synthesis of lipid nanoparticles thanks to its unique ability to cause rapid and homogeneous nanoparticle self-assembly, leading to excellent size control and uniformity, and high encapsulation efficiency. As this method is based on rapid microfluidic mixing, research articles generally only focus on the mixing conditions (TFR, FRR) impact on the nanoparticle properties but tend to overlook other external factors such as chip characteristics, N/P ratio or dialysis (or more generally purification process).
In this study, the authors present the impact of the dialysis on the nanoparticle parameters, as well as its possible interaction with TFR and FRR using a design of experiment approach and quantify the influence of each variable.
Aims:
- Studying the impact of dialysis on nanoparticle final characteristics
- Estimating the influence of TFR and FRR on the final nanoparticle characteristics with and without dialysis
Experimental Setup | Lipid mix and microfluidic system
The LNPs were prepared using microfluidic ethanol injection method. LNP were composed of a mix of DOTAP (cationic lipid), DSPC, Cholesterol and DSPE-mPEG2000 at a molar ratio of 40: 10 : 48,5 : 1.5, dissolved into ethanol at a 2,5 mM concentration. The aqueous phase consisted of citrate buffer at 1mM.
The microfluidic setup was made of a staggered Herringbone mixer (Fluidic 187, Microfluidic Chipshop) for the mixing of the 2 solutions and a high accuracy flow control system (Inside Therapeutics) for the precise control of the environment parameters.
To study the influence of the mixing conditions parameters, TFR in the range of 0,4 to 4 mL/min were tested, with FRR between 3 and 9, and characterized using DLS systems.
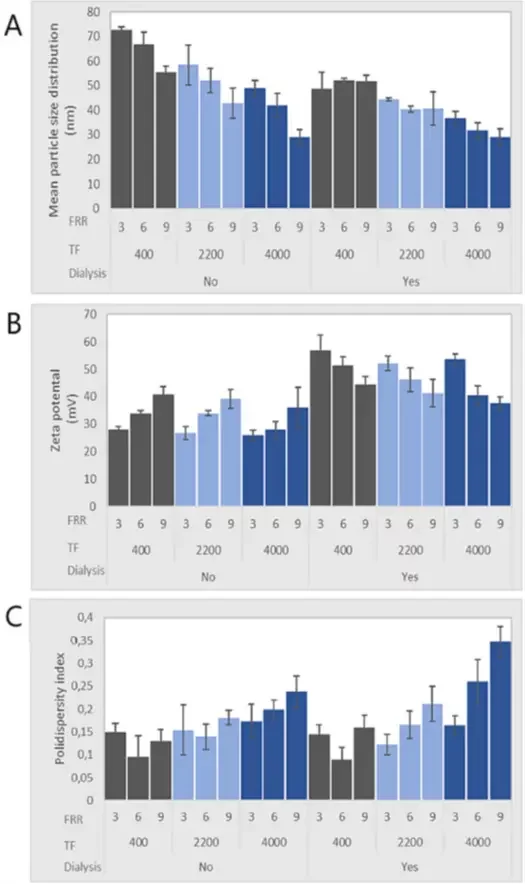
Key findings | Particle size, Zeta potential and PDI
As introduced above, 3 main nanoparticles characteristics were studied: particle size, Zeta potential and polydispersity index.
Particle size:
As introduced in the figure below, dialysis caused a large reduction in the average size of the nanoparticles – and this for nearly all synthesis conditions. Regarding synthesis variables, and consistently with already published papers and our review on the fundamentals of nanoparticle synthesis, nanoparticle size tends to decrease at higher TFR in a herringbone mixer – this both with and without dialysis.
However, one key finding is that, while before dialysis the FRR has a major influence on the final nanoparticle size, its impact is greatly reduced post dialysis.
Finally, it also appears that dialysis also helps with process repeatability, with better batch to batch repeatability after than before dialysis.
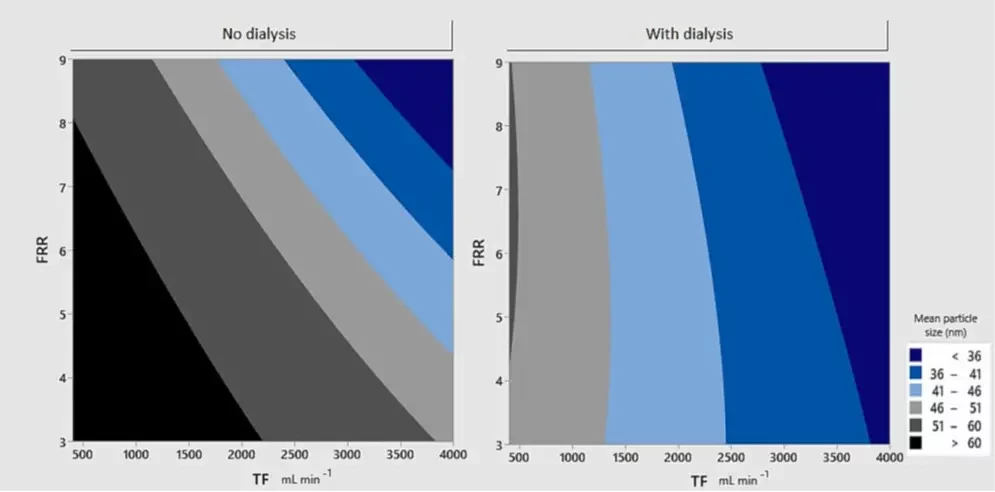
Conclusions | Dialysis, a parameter that should be taken into account from the start
Same formulation and similar experimental procedures (except from dialysis) could lead to completely different LNPs systems.
The very different effect of FRR before and after dialysis for size and zeta potential shows that dialysis should be a necessary step after synthesis in screening stages, as the knowledge gathered from its characterization before dialysis becomes insignificant after. More generally, because of parameters interaction, the largest number of synthesis parameters should be considered for preliminary studies to ensure best reproducibility all throughout development stage.
The below chart summarizes the impact of the different synthesis parameters on the final nanoparticle characteristics:

Are you interested in microfluidics methods to manufacture LNPs?
Reference:
Ronny Vargas, Miquel Romero, Tomás Berasategui, David A. Narváez-Narváez, Patricia Ramirez, Anna Nardi-Ricart, Encarna García-Montoya, Pilar Pérez-Lozano, Josep Mª Suñe-Negre, Cristina Moreno-Castro, Cristina Hernández-Munain, Carlos Suñe, Marc Suñe-Pou,
Dialysis is a key factor modulating interactions between critical process parameters during the microfluidic preparation of lipid nanoparticles,
Colloid and Interface Science Communications, Volume 54, 2023, 100709,
https://doi.org/10.1016/j.colcom.2023.100709
